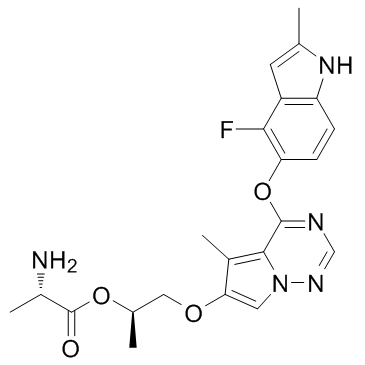
Brivanib alaninate
CAS No. 649735-63-7
Brivanib alaninate( BMS-582664 | BMS 582664 | BMS582664 )
Catalog No. M15466 CAS No. 649735-63-7
A prodrug of Brivanib, which is a dual inhibitor of VEGFR2 and FGFR1 with IC50 of 25 nM and 148 nM respectively.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 2MG | 73 | In Stock |


|
| 5MG | 105 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 189 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 338 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 551 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 878 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameBrivanib alaninate
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionA prodrug of Brivanib, which is a dual inhibitor of VEGFR2 and FGFR1 with IC50 of 25 nM and 148 nM respectively.
-
DescriptionA prodrug of Brivanib, which is a dual inhibitor of VEGFR2 and FGFR1 with IC50 of 25 nM and 148 nM respectively; exhibits improved aqueous solubility and oral bioavailability of the parent compound.Liver Cancer Phase 3 Clinical(In Vitro):Brivanib inhibits VEGFR1 and FGFR-1 with IC50 of 0.38 μM and 0.148 μM. Brivanib is not sensitive to PDGFRβ, EGFR, LCK, PKCα or JAK-3 with IC50 all above 1900 nM. Brivanib could inhibit the proliferation of VEGF-stimulated HUVECs with IC50 of 40 nM, compared to 276 nM in FGF-stimulated HUVECs. On the other hand, brivanib exhibits low activity to tumor cell lines. Brivanib doses ≤20 μM paradoxically enhances FGF-induced LX-2 cell proliferation, whereas higher brivanib doses (≥30 μM) inhibits LX-2 cell proliferation. The inhibitory effect of brivanib on liver fibrosis is not through inhibition of TGF-β 1-induced stellate cell activation, and is possibly through inhibition of PDGF-BB-induced stellate cell activation. (In Vivo):Brivanib displays antitumor activities in H3396 xenograft in athymic mice. At a dose of 60 and 90 mg/kg (p.o.), brivanib completely inhibits the tumor growth, with TGI of 85% and 97%, respectively. Moreover, brivanib significantly suppresses tumor growth in Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) xenografts, which due to the decrease in phosphorylation of VEGFR2. The results show that the tumor weights in 06-0606 xenograft mice are 55% and 13%, compared with the controls at a dose of 50 mg/kg and 100 mg/kg. Brivanib is suggested to be efficient in treatment of HCC. Brivanib (50 mg/kg, p.o.) attenuates liver fibrosis and stellate cell activation induced by BDL in mice. Brivanib inhibits growth factor and growth factor receptor mRNA expression in sham control animals but shows variable effects in bile duct ligated animals.
-
In VitroBrivanib inhibits VEGFR1 and FGFR-1 with IC50 of 0.38 μM and 0.148 μM. Brivanib is not sensitive to PDGFRβ, EGFR, LCK, PKCα or JAK-3 with IC50 all above 1900 nM. Brivanib could inhibit the proliferation of VEGF-stimulated HUVECs with IC50 of 40 nM, compared to 276 nM in FGF-stimulated HUVECs. On the other hand, brivanib exhibits low activity to tumor cell lines. Brivanib doses ≤20 μM paradoxically enhances FGF-induced LX-2 cell proliferation, whereas higher brivanib doses (≥30 μM) inhibits LX-2 cell proliferation. The inhibitory effect of brivanib on liver fibrosis is not through inhibition of TGF-β 1-induced stellate cell activation, and is possibly through inhibition of PDGF-BB-induced stellate cell activation.
-
In VivoBrivanib displays antitumor activities in H3396 xenograft in athymic mice. At a dose of 60 and 90 mg/kg (p.o.), brivanib completely inhibits the tumor growth, with TGI of 85% and 97%, respectively. Moreover, brivanib significantly suppresses tumor growth in Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) xenografts, which due to the decrease in phosphorylation of VEGFR2. The results show that the tumor weights in 06-0606 xenograft mice are 55% and 13%, compared with the controls at a dose of 50 mg/kg and 100 mg/kg. Brivanib is suggested to be efficient in treatment of HCC. Brivanib (50 mg/kg, p.o.) attenuates liver fibrosis and stellate cell activation induced by BDL in mice. Brivanib inhibits growth factor and growth factor receptor mRNA expression in sham control animals but shows variable effects in bile duct ligated animals.
-
SynonymsBMS-582664 | BMS 582664 | BMS582664
-
PathwayAngiogenesis
-
TargetVEGFR
-
RecptorFGFR1|Flk1|VEGFR1|VEGFR2
-
Research AreaCancer
-
IndicationLiver Cancer
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number649735-63-7
-
Formula Weight441.4555
-
Molecular FormulaC22H24FN5O4
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
Solubility10 mM in DMSO
-
SMILESCC1=CC2=C(N1)C=CC(=C2F)OC3=NC=NN4C3=C(C(=C4)OCC(C)OC(=O)C(C)N)C
-
Chemical NameL-Alanine, (1R)-2-[[4-[(4-fluoro-2-methyl-1H-indol-5-yl)oxy]-5-methylpyrrolo[2,1-f][1,2,4]triazin-6-yl]oxy]-1-methylethyl ester
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1. Cai ZW, et al. J Med Chem. 2008 Mar 27;51(6):1976-80.
2. Huynh H, et al. Clin Cancer Res. 2008 Oct 1;14(19):6146-53.
3. Patel RR, et al. Eur J Cancer. 2010 Jun;46(9):1537-53.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Regorafenib hydrochl...
Regorafenib hydrochloride (BAY73-4506) is a potent, orally active multikinase inhibitor.
-
Telatinib
An orally active, small molecule inhibitor of VEGFR-2 (IC50=6 nM), VEGFR-3 (IC50=4 nM), PDEGFRα (IC50=15 nM) and c-Kit (IC50=1 nM) in biochemical assays.
-
SU 4981
SU 4981 is an inhibitor of VEGFR and a modulator of tyrosine kinase activity.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


